FTC Compute Move Distance 20221014
From wikidb
Contents
Lab 3: Compute Distance
Beginning Notes
Why
- Where am I? is a key question a robot must know to get some things done.
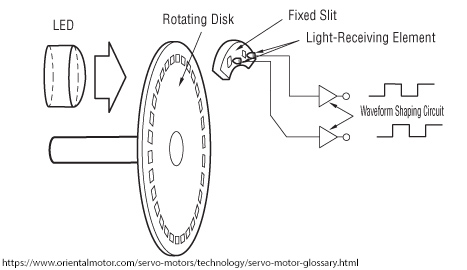
- Odometry is the use of sensor data to estimate a robot's position: Odometry from Wikipedia.
- An encoder is an example sensor that can be used to answer that question: Encoder from Wikipedia.
- Dead reckoning is figuring out where you are based on where you were and your estimate on how far you moved in some direction: Dead Reckoning from Wiipedia.
Check Points
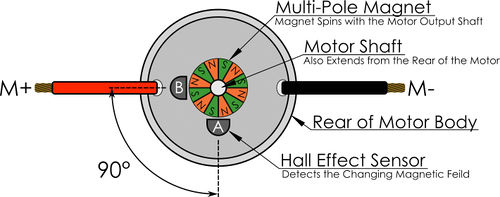
- Locate the Core Hex Motor (REV-41-1300) on the REV Robotics web site. What is the encoder count for one shaft out revolution?
- What is the diameter of a REV-41-1354 Traction Wheel?
- How far does the robot go with each revolution of this wheel in? (Compute the wheel's circumference.)
- Convert the circumference from millimeters to inches.
- Compute how far does the robot moves in 1000 encoder counts.
- Measure how far the robot move in the MotorPositionEpp.java to check your answer to check your answer.
Check Points
Run an Example Program
- Code based on FTC_Motor_Encoders_20200304
References - Digging Deeper
- DC Motors
- Using Encoders
- Autonomouse Navigation OnBot
- For Java code see: "Setting Velocity" subsection in the program "HelloWorld_EncoderAuton".
- There is also subsection labeled "Turning the Divetrain Using RUN_TO_POSITION"
- There is also an earlier sections called "Moving to a Target Distance."